What is a Solar Inverter? A 2026 Guide (Types & Cost)
Ever wondered how your home’s power is actually extracted from the sunlight of your solar panels? The majority of homeowners pay attention to panels but forget to mention the solar inverter as the smart technology to makes solar energy a possibility. And without it, your panels are nothing but drowning in the sun and having no place to discharge the power.
A high-efficiency inverter is the hidden powerhouse that transforms sunlight into electricity and maximizes the output of your system and assists you in saving more on your power bills. We shall discover how this smart device turns the sunshine into eco-friendly power for your home.
What is a Solar Inverter? Quick Facts
- Simple Answer: The inverter is the “brain” of your solar system.
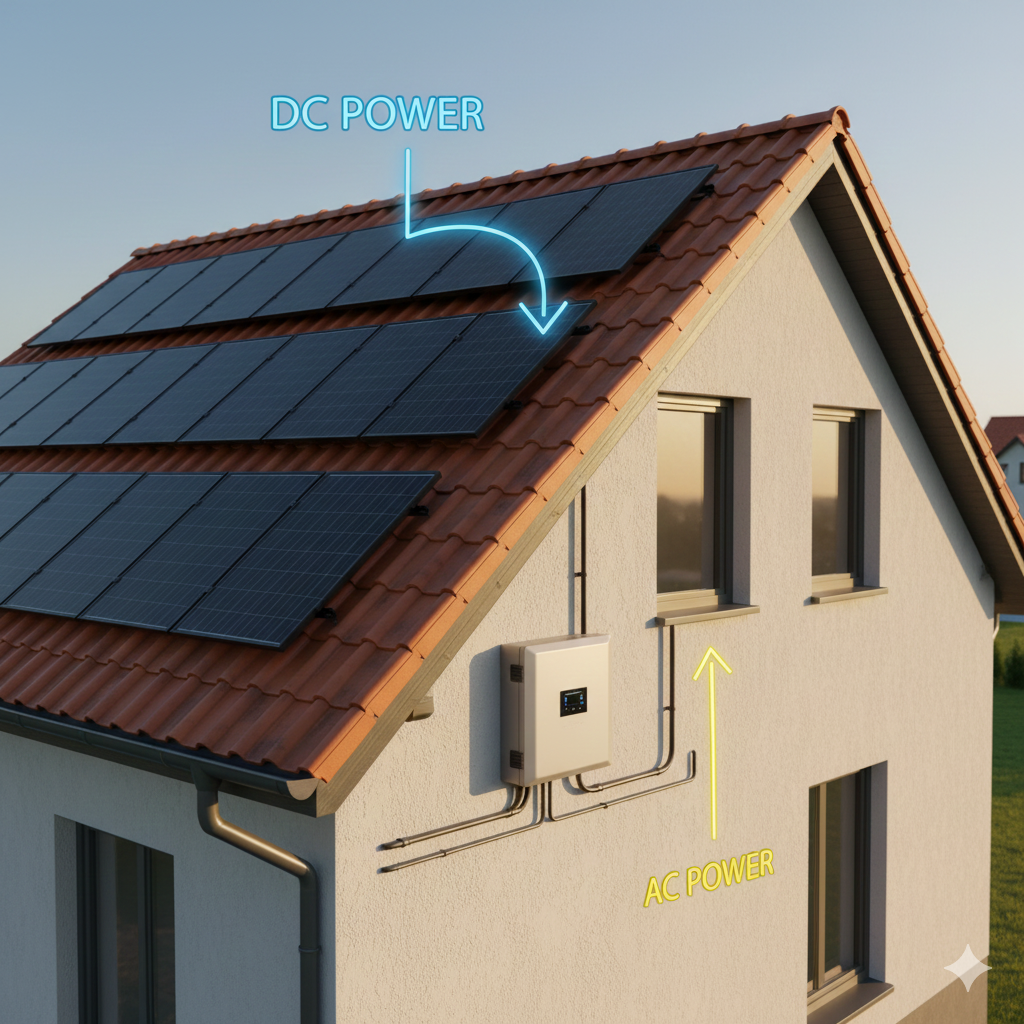
- Main Job: It converts the Direct Current (DC) power from your solar panels into Alternating Current (AC) power that your home can use.
- Safety Role: It also manages system safety and shuts down power during a grid outage to protect utility workers.
- The “Bridge”: The *type* of inverter you choose (like a “hybrid” inverter) is what makes your system “battery-ready.”
Have Questions About Your System?
Our in-house experts can help you choose the right inverter, or quote a complete system. Contact us today for a free, personalized consultation.
Introduction
Using solar panels to power your home does not just mean being able to capture the sunlight and then using it but it is also about the ability to convert it into useful energy. And this is where the solar inverter comes in which can be considered the brain and the heartbeat of any solar system. It is the only way that the clean energy generated by your panels would not go to waste in the form of useless direct current (DC). This is a small but mighty device that converts DC to alternating current (AC) which is the same type of electricity that runs your lights, appliances and life.
The role of a solar inverter in the contemporary booming solar market has never been as important as it is today. SEIA suggests that by 2030, 10 million residential solar systems would be installed. These numbers have already made homeowners more aware of the fact that the quality of inverters determines the performance of the system and long-term savings. Residential string inverters have an average lifespan of 10-15 years and your solar panels should last 25-30 + years, so chances are that your inverter will be dead way before your panels.
Nedes.us is a renewable energy engineering expert and in this guide with 10 years of experience in designing solar arrays in residential and commercial buildings, how it works, what it costs and where it is going. To understand how inverters fit into a home solar system, see our guide on types of residential solar systems
Have a Technical Question?
Have a complex project? Our in-house engineers are ready to discuss your technical requirements for solar, design, and storage.
What Is a Solar Inverter?
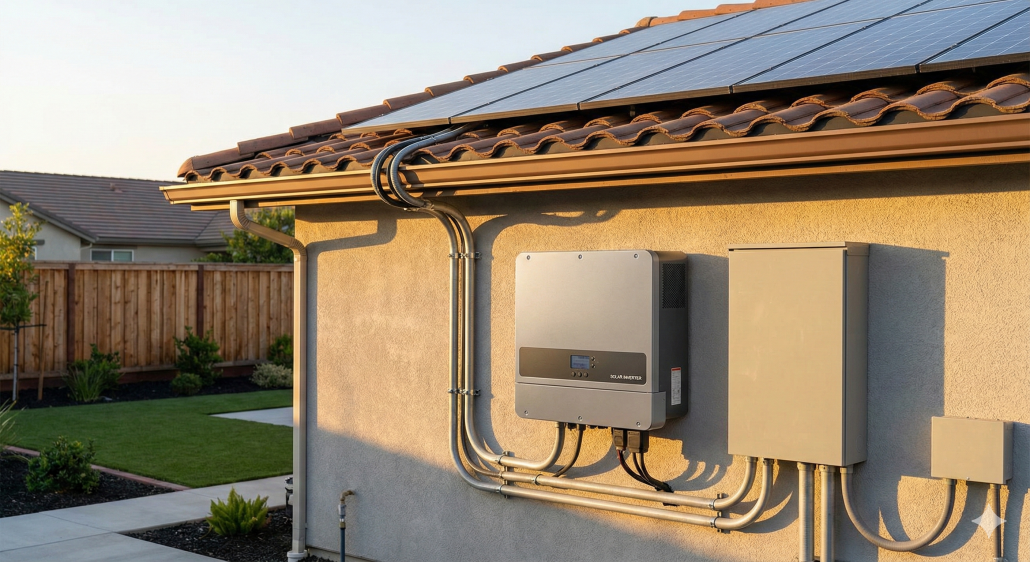
Then what is a solar inverter and why is it so important? Differently put, it is the smart-looking device that transforms the direct current DC power from your solar panels into alternating current AC the one which your home and appliances operate on daily. It is with his conversion that all the sunlight that is captured would turn into untapped energy.
A solar panel inverter is a device that connects your panels to your power system. It assures maximum conversion of all the watts of the sunlight and proper delivery of it, maximizing the output and detecting any problem before it can affect performance.
According to the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), modern photovoltaic inverters have amazing efficiency with an average efficiency of 98% and a maximum efficiency of 95-99%. It translates to the fact that nearly all the energy generated by your panels will be converted into useful power resulting in the solar energy inverter being an essential component of long-term savings and system stability. Choosing the right inverter is especially critical when planning for off-grid solar system services.
How Does It Work? (The Technology Behind It)
How does the sun change into electricity that lights your place of residence? It begins by having your solar panels absorb sunlight and production of direct current (DC) electricity. This is where the photovoltaic inverter also known as a solar converter, enters the picture.
Step by step: DC electricity will run out of your panels into the inverter and it will be converted into alternating current (AC) the one used by your appliances and the electric grid. The inside contains elements such as transformers and transistors that maintain that power, control the flow and make the most of the energy, so that as much power as possible is used.
Practically the inverters do not have the same lifespan as the panels. Whereas the lifespan of solar panels is 25 or more years and the average life of a string inverter is 10-15 years. This renders it significant to keep a track of the performance and schedule maintenance or upgrades.
In summary, a photovoltaic inverter is the one that connects the sun’s energy and the energy that can be utilized in day-to-day lives and silently striving to transform sunlight into dependable power.
Types of Solar Inverters
The selection of the appropriate inverter is essential to maximise your solar investment. There are several products in the market and knowing the types of solar inverters you will have is a guarantee that you will have the right solution for your domestic or commercial establishment. There are strengths, weaknesses and best applications of each type of inverter both in small residential systems and large business installations.
String Inverters
String inverters are the most common choice for residential solar systems. They are joined together into one inverted structure with a series of solar panels.
Summary
Pros: It is cost-effective, simple installation and is dependable.
Cons: Performance may decrease in case one of the panels is shaded or performing poorly.
Best Use: Uniform rooftops without much shading.
Microinverters
Microinverters are compact inverters that are clamped to the panel which are known to transform DC to AC on a one-on-one basis.
Summary
Pros: Can maximize the amount of power obtained due to shady or lop-sided roofs, easy to monitor can track panel performance.
Cons: It is more expensive to acquire and there are additional parts to service.
Best Use: Shaded roofings, complicated designs or in case of future expansion.
Power Optimizers (Hybrid Inverters)
Hybrid inverters with power optimizers combine traditional string inverter efficiency with panel level optimization.
Summary
Pros: Cheaper and efficient in price can be used with battery storage and better energy capture in partial shade.
Cons: It is a little expensive when compared with string inverters and it needs expert installation.
Best Use: Homes intending to incorporate battery storage or even average shaded roofs.
Central Inverters
Central inverters are large-scale devices mostly applied in commercial and utility-scale solar systems.
Summary
Pros: Large array is cost-effective, scalable and strong.
Cons: It does not apply to small residential roofs and shading affects the whole system.
Best Use: Commercial or industrial installations that are large.
Grid-Tie Inverters
Unwanted energy goes to grid-tie inverters which operate excess energy back to the electrical grid enabling homeowners to obtain credit or cut electricity bills.
- Pros: Optimizes the use of the energy available, net metering is made possible and very efficient.
- Cons: It needs a grid connection and might not be able to supply power backup when there is an outage.
- Best Use: Residential or commercial grid-connected systems that are interested in optimizing savings.
| Inverter Type | Pros | Cons | Best Use Case |
| String Inverter | Cost-effective, reliable | Shading impacts performance | Uniform roofs, simple systems |
| Microinverter | Panel-level optimization, monitors | Higher cost, more components | Shaded or complex roofs |
| Hybrid / Power Optimizer | Battery-ready, partial shade-tolerant | Slightly more expensive | Homes with battery plans |
| Central Inverter | Scalable, cost-efficient for large arrays | Not for small residential roofs | Commercial / utility-scale systems |
| Grid-Tie Inverter | Net metering maximizes savings | Grid-dependent, no backup during outage | Grid-connected homes or businesses |
How to Choose the Right Inverter for Your Home?
The selection of the right inverter can make or break your solar investment. The range of a good solar panel inverter guarantees the conversion of energy to maximum, long-term efficiency and optimal savings. There are various alternatives available in the market, so it will save you time and money to know what to search for.
Key Selection Criteria
Efficiency Matters: Solar power inverters with high conversion efficiency of at least 95-98% mean that there is minimal energy loss.
Size and Compatibility: Select any inverter according to the panel output of your system. Small inverters may prevent large production and large models may make the initial investment unnecessary.
Warranty and Reliability: Check the warranty period and most reputed brands offer 10-25 years depending on the type of inverter. A greater warranty length is an indication that the quality of the building was high and the manufacturer is confident.
Monitoring and Features: Modern solar power inverters for the home frequently have WiFi monitoring, performance monitoring and fault alerts. These are characteristics that enhance better management of systems and the early identification of problems.
Battery-Ready Options: If you want to add energy storage or a hybrid system and choose an inverter that supports batteries or hybrid systems later.
Installation and Maintenance: Have certified installers working on the job who are either nationally/regionally certified and are safety and compliance-minded.
Cost Example
The standard residential models of inverters range between $1000 and $3000 with the average of inverters between $2000 and $3000 based on the type and features. The planning of his costs assists the homeowners to plan well with regard to budgeting and taking into consideration the installation and occurrence of maintenance.
The planning of his costs assists the homeowners to plan well with regard to budgeting and taking into consideration the installation and occurrence of maintenance.
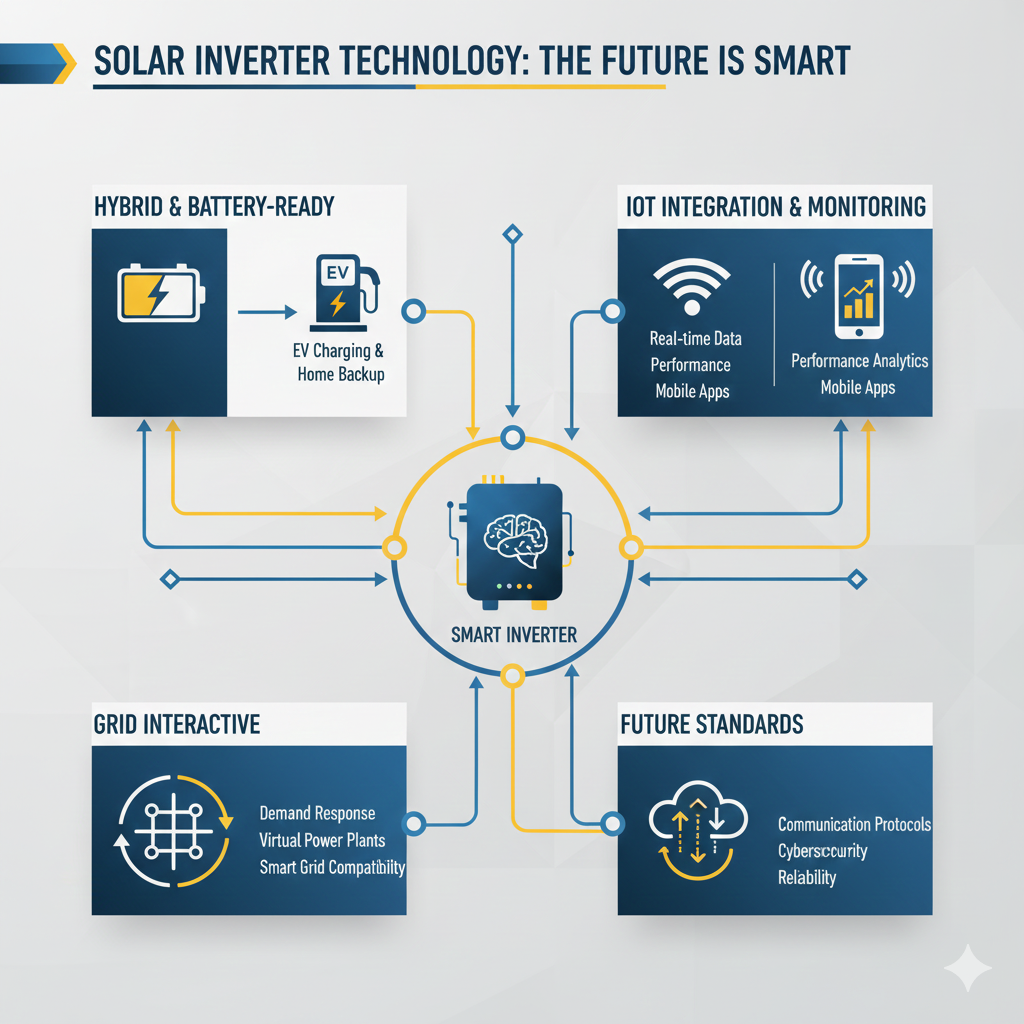
Smart Technology and Future Trends in Solar Inverters
Smart solar inverters have given a future to solar energy. These devices are more than just converting electricity. They measure, streamline and integrate your system with applications and IoT, placing the power in the hands of the homeowner as they make their energy usage more efficient. Current solar power inverters use smart technology and add future-compatible features such as battery usage and grid interaction.
Hybrid and Battery-Ready Inverters
Hybrid inverters can intelligently manage energy between solar panels, domestic needs and battery storage. They enable you to save excess energy for later use and enhance savings. They can also be easily integrated with electric vehicle (EV) charging systems. When it comes to selecting an inverter and it is important to choose a battery ready one to avoid future upgrades.
IoT Integration and Monitoring Apps
Smart inverters usually have WiFi and monitoring applications. These tools will warn you about failures, streamline operations and power analytics. Such monitoring enhances uptime, system reliability and user interaction.
Sunrun says that
Today’s inverters come with built-in WiFi monitoring, which can alert you to faults, optimize performance and feed data for system analytics.
Grid-Interactive Technology
Grid-interactive inverters enable homeowners to sell surplus power, engage in demand response programs and meet changing utility regulations. This will not be the most efficient use of energy but it will also future-proof your system to integrate with the smart grids.
Industry Standards
It is important to be on the industry standards. Major producers like Enphase or SolarEdge consistently introduce firmware changes and technical instructions to improve the safety and efficiency. Use of smart solar inverters would mean that you are compliant with grid codes and your system is up to date and trusted.
Installation and Maintenance Real-Life Example
The maintenance and the correct installation are what will assure you of the optimal efficiency of your solar system. The selection of the appropriate solar panel inverter for your house can have a great impact on performance, overall power output and long-term savings. The following is a real-life case of how a careful choice of an inverter and its care can make a difference.
Real-Life Case Study of Where Shaded Roof Home
A homeowner with a complicated shade design had to get a solution that would not dissipate energy as a result of shading. They then chose microinverters which are installed on an individual basis after consulting with a certified installer.
- Selection Reason: Microinverters enable the optimization of panels at the panel level for example, shaded panels do not negatively impact the overall system.
- Cost: The total inverter hardware cost amounted to approximately $2200 on 20 panels which is in line with average inverter costs in the home.
- Performance: During the initial three years the system averaged 98% efficiency which demonstrated that microinverters were the most efficient to produce maximum power even in partial shade conditions.
Maintenance Tips for Long Term Performance
Periodic checks exclude the possibility that your inverter for solar panels is still working at the highest level:
Visual checks: Check against physical damage, dust, debris or moisture.
Monitoring: Inverter apps or dashboards can be used to monitor performance, identify errors, and get notifications.
Warranty: The majority of inverters are provided with 10-15 year warranties; they are subject to check what is warranted, repaired and labor.
Replacement Timeline: Strategy is to swap string or typical inverters at 10-15 years of age whereas microinverters can outlast at times 15-20 years.
Lead into Action
Need to make sure that your solar system works optimally? Our professional advice on selecting the appropriate solar panel inverter and system setup to install in your home and a quote is obtained through our certified estimating service.
Conclusion
Solar inverters are the intelligent technology used to convert the sunlight into usable energy which makes the homes very efficient in terms of saving energy and in the long run. The selection of a suitable solar panel inverter or inverter of solar panels is not only important to its performance in the present context but also to ensure that the system can be extended to battery storage, EV charging and integration with the smart-grid in the future.
Supported by industry data provided by NREL and EnergySage and described by our own estimating experts, this guide will give you all the details of the selection, installation and maintenance of your solar power system. Make the smartest investment in your home’s energy future today.
The solar inverter is one of the most critical components of a solar energy system. The U.S. Department of Energy explains its main job: converting the Direct Current (DC) electricity from your panels into Alternating Current (AC) electricity that your home can use.
FAQS
What does an inverter do?
A solar inverter changes DC electricity into AC electricity that can be used by your home and the electric grid produced using solar panels. This is the fundamental role of any inverter and the reason why it is needed by solar energy systems.
What are the types of inverters in solar systems?
Solar inverters are available in various types that are specific to the needs of multiple systems:
String Inverters: Low-priced and suitable for continuous roofs.
Microinverters: Panel-level optimization, perfect for shaded or complex roofs.
The Power Optimizer/Hybrid Inverters: String and panel level with battery-ready.
Central Inverters: Central inverters are applied to systems in commercial or utility-scale applications.
What is the lifespan of a solar inverter?
Replacement planning is useful in ensuring efficiency and the extended longevity of the panels. There are many types of solar panel inverters with a range of lifespans:
String Inverters: Basically 10–15 years.
Microinverters: Have a life span of 15–25 years or above.
What is the approximate cost of a solar inverter replacement?
The cost of replacement residential inverters is between $1000 and $3000 with an average of about $2000 depending on the type and features. These consist of regular string inverters and micro inverters.
Should I upgrade my inverter to upgrade solar panels or add batteries?
Yes. New smart solar inverters and hybrid/battery-ready inverters can optimize power storage, interoperate with EV charging, and increase the system efficiency. The future-proofing of your solar system by upgrading it makes it high-performing. The keyword to be used is smart solar inverter.