How Many Watts Does a House Use? (A 2026 Guide to Sizing)
Did you ever ask yourself why your electricity and energy bills continue to grow month after month yet you barely use lights and other electrical appliances? The thing is that the overwhelming number of homeowners do not even know the amount of wattage that their home actually consumes and the amount of power that the daily appliances quietly consume. Regardless of whether you have a tiny house or a large house, the initial step towards saving energy, reducing expenses and strategizing on more intelligent ways to generate energy such as solar power is knowing your average power use.
Home Wattage: Quick Facts
- Watts (Instant Power): An average home may use 2,000-6,000 watts at any given moment, with a “peak” load of over 10,000 watts if the A/C and oven are on.
- Kilowatt-Hours (Total Energy): The more important number is on your bill. The average U.S. home uses about 29-30 kWh per day.
- The “Bridge”: Knowing your daily kWh usage is the #1 step in correctly sizing a solar panel and battery system to eliminate your bill.
Introduction
Understanding Your Home Power Needs
Ever wondered how much power your home really uses from LED bulbs to air conditioners? To the majority of homeowners, it comes as a surprise to discover that the current energy habits they engage in on a daily basis actually amount to thousands of watts of power consumed on a daily basis. It is not only about curiosity as knowing how many watts a house consumes but also about being in control, efficient and more intelligent in its energy planning. Your energy consumption is a factor in calculating local costs, such as the electricity rates in Lawton, OK.
The US Energy Information Administration estimates that an average household in the United States uses an annual 10500 kWh of electricity. It is the same as having a 1000-watt appliance running almost 6 months a year. This understanding reveals the cumulative effect of the use of everyday appliances such as a fridge, a microwave, an electric space heater etc, on your total average home power usage.
With the energy prices on the ascendancy and sustainability being the focus, knowing your home’s wattage can save you some money, correctly size your solar system and even make backup power plans. This is a manual that our professional Energy Consultant and Solar Specialist designed by dividing real-life information, details given by experts and practical applications to assist you in calculating and controlling your electricity consumption.
Get a Professional Energy Analysis
Our experts can analyze your home’s energy bills to show you exactly what size system you need to cover your wattage and save money.
Understanding Watts, Kilowatts and kWh
The Building Blocks of Energy
You can not gauge the amount of electricity being consumed in your home before you know what a watt is. It can be said that a watt is a measure of power or that power is the rate at which energy is consumed at a given time. Imagine it like a speedometer of electricity like a 60 watt LED bulb consumes energy at a steady rate of 60 watts per hour while it is on.
A kilowatt is just 1000 watts and this greater amount of measurement makes it easier to measure the power of houses or appliances. To illustrate when you combine a few appliances that may operate simultaneously at home such as lights, refrigerator and air conditioner the total draw of these may be 1.25 kW at a specific time.
As concerns your electric bill and you will look at kilowatt hours (kWh), which is power by time. It is the amount of electricity consumed throughout. An example is in case your home has an average of 900 kWh per month like 30 kWh per day or an average continuous load of 1.25 kW based on US Energy Information Administration data.
To put it simply:
- Watts = Power used instantly.
- Kilowatt = 1000 Watt
- Kilowatt hours = Total power consumed over time.
Appliance Wattage Breakdown
A Real Example of How Much Power Your Home Uses
Wondered which gadgets were quietly increasing your electric bill? Appliance knowledge is paramount in knowing how many watts a house uses and how to plan either in terms of efficiency, saving energy or putting up solar systems. The following is a breakdown of real-world examples of common household appliances and their common energy consumption.
Lighting LED Bulbs vs Incandescent Lights
Lighting is a factor that is not taken seriously yet can contribute to much of the day-to-day energy consumption.
LED Bulb: 10-15W, enormously energy saving, durable and efficient.
Incandescent light bulb: 60-100W, much less efficient and more power is used on a daily basis. The LED lights enable the reduction of the amount of energy consumed by lights by a minimum of 75%.
Kitchen Appliances: Microwave and Refrigerator
Kitchen electricals are operational on a daily basis and they contribute to daily home power consumption to a large extent.
Refrigerator power consumption: 150-400W, constant-on and daily consumption goes behind 1.5 to 3 kWh.
Microwave wattage: 800-1200W convection microwave a little higher, typical usage 1h/day and 1-2kWh.
The fact of knowing the number of watts a microwave heats or the number of watts a refrigerator heats will help in the proper calculation of the energy needed by a home.
Washing and Personal Care: Washing Machines and Hair Dryers.
Most of the high-wattage appliances are optimally energy consuming only at short intervals.
Washing machine: 500-1000W per load and daily kWh varies depending on how it is used.
Best hair dryers: 1200-1875W and short bursts but significant wattage. By restricting the number of people using a household at once or by converting it to devices with lower power consumption and one can minimise the average home power usage and avoid peak load demands.
Get a Free Energy Analysis Now
Call our team for a free, no-obligation consultation. We can perform a detailed energy audit for your home right over the phone.
Heating and Cooling An Electric Space Heaters and Indoor Heaters
Most households consume more electricity during heating and cooling.
Electric space heater / indoor heater: 1500W+ and 4-6 hours/day has a potential of 6-9 kWh/day.
Air conditioning units: 2000-4000W based on size and efficiency.
This supports the idea of why HVAC systems are the biggest energy expenditures of the home and why intelligent scheduling or solar-powered solutions can be significant.
Entertainment and Electronics like TVs
Electronics may be small but when some devices operate simultaneously it accumulates.
TV power: 100- 200W, daily power savings 5 hours 0.5 1 kWh.
Understanding how much electricity a TV uses enables the homeowner to plan on power usage and find possible areas of energy saving.
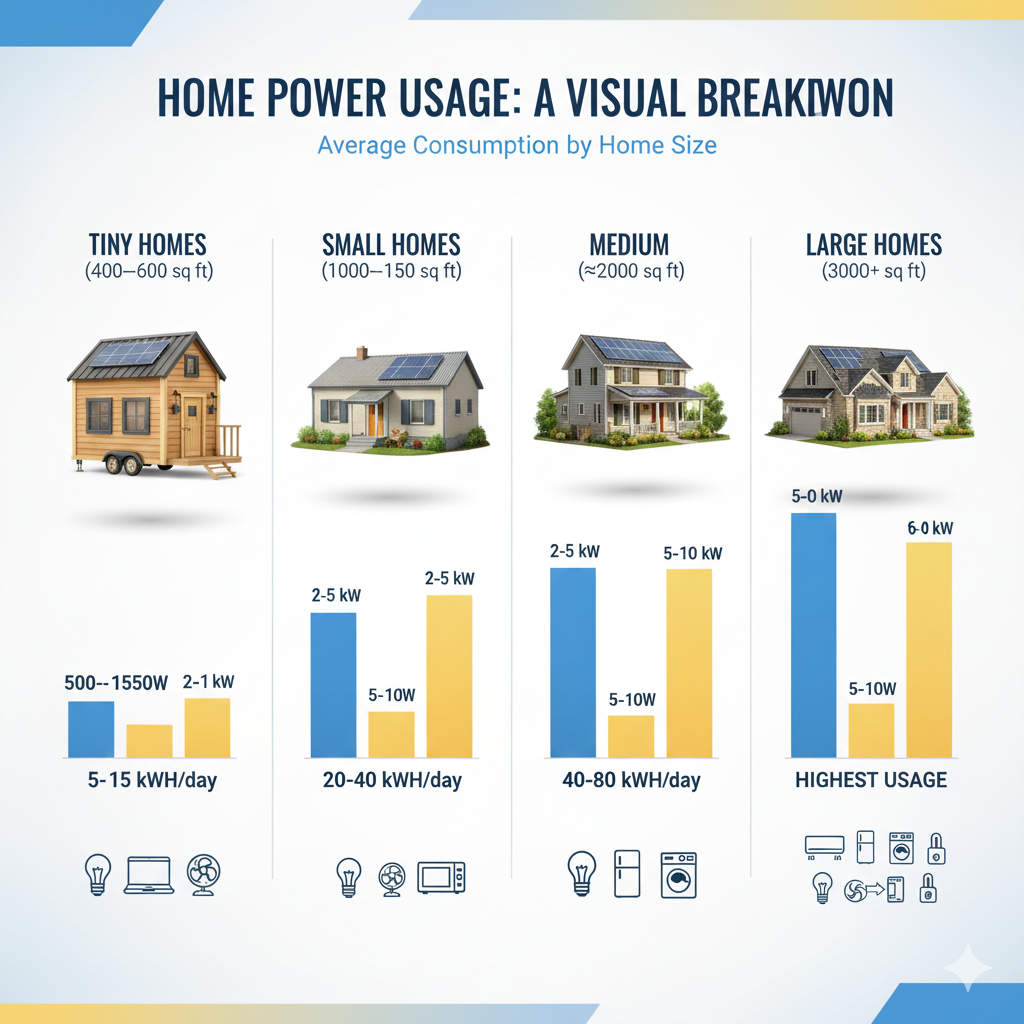
Average Home Power Usage by Size and Identify Your Home Category
The first thing you should do to control bills and plan better solutions is to understand the energy consumption of your home. The number of watts that a house consumes can be quite different depending on the size of your house. We will start with the breakdown of the common power usage of the various sizes of homes so that you can determine which home type you are in.
Tiny Homes (400–600 sq ft)
Small houses are relatively environmentally friendly in their construction as they require significantly less energy compared to bigger homes.
- Average power use: 500-1500W
- Example load: LED lights, laptop and fan
- Estimated Daily use: 5-15 kWh
They are the perfect houses to live in with low energy consumption and typically accompany a small-scale solar solution to save money.
Small Homes (1000–1500 sq ft)
The middle energy needs of small houses may be moderate, but they may have a huge electricity bill in case running appliances are used simultaneously.
- Average Power Use: 2–5 kW
- Example: Load the Microwave, fridge and TV.
- Estimated Daily Use: 20–40 kWh
These numbers assist the homeowners in their planning of efficient use of appliances and in estimating the requirements of solar panels.
Medium Homes (≈2,000 sq ft)
Medium-sized houses can be considered a characteristic of the US households with increased energy needs.
- Average power use: 5-10 kW
- Example Load: Washer, heater and air conditioning
- Estimated Daily Use: 40-80 kWh
The average home power usage can be cut by proper and effective energy planning such as smart thermostats or power-saving home appliances.
Large Homes (3,000+ sq ft)
Large homes consume the most electricity particularly the large powered appliances and central heating, ventilation or air conditioning systems.
- Average Power Use: 10–15 kW
- Example Load: central HVAC and pool pump.
- Estimated Daily Use: 80–120 kWh
In the case of such homes, the higher electricity expenses can be countered by investing in Solar Energy Systems in Large Homes so that they will not be dependent on the grid.
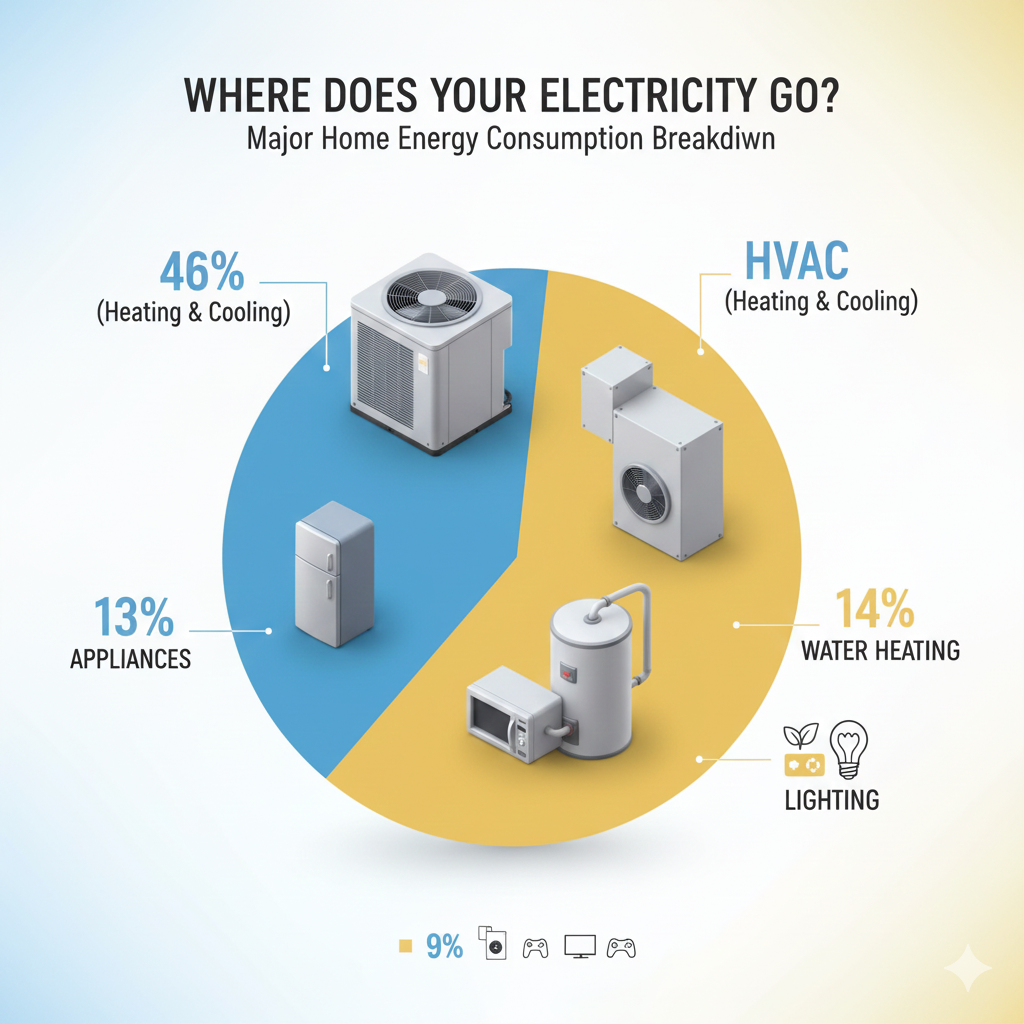
What Uses the Most Electricity in a Home to Identify Energy Hogs?
Wonder why you are paying more than you thought for electricity? Knowing what consumes the most electricity in your home can assist you in identifying the hogs of power and be in control of your average home power consumption. As stated by the US Energy Information Administration, household energy consumption consists of a small number of dominant categories.
HVAC Systems: The Biggest Energy Consumer
Heating, ventilation and air conditioning systems consume almost one-half of home energy consumption 46%. HVAC systems consume the greatest amount of power both in summer because whether you need to warm your home in winter or cool it in summer, the systems are on all the time.
Water Heating Where Hot Water Is With a High Cost
Approximately 14% of the household consumption is water heating. Showering, washing of utensils and laundry are expensive. Enhancing the efficiency of your current water heater or toilet to energy-efficient ones will save the number of watts used by a house with no sacrifice.
Appliances: Everyday Energy Draw
Appliances used in the home take up approximately 13% of the energy expenditure. Refrigerators, microwaves and washing machines are the types of appliances that are used on a regular basis and their daily usage contributes greatly to daily wattage. Tracking the refrigerator wattage, the microwave wattage and the washing machine consumption assists the homeowners in maximizing the use of energy.
Lighting Bright Ideas That Save Energy
Lighting accounts for approximately 9% of home electricity use.
By replacing your incandescent light bulbs with LED bulbs and switching off unnecessary fixtures, your lighting usage will decrease by 50-75% of your household’s average power consumption.
Electronics A Small Devices and Big Impact
Electronics such as TVs, computers and gaming consoles make up 8% of household energy use.
Some electronics even when idle, attract standby power. Knowing how much electricity a TV uses or other devices would help determine which areas to unplug or buy new models that consume less energy.
Pro Tip
By concentrating on these best energy types, you can concentrate on saving, lowering bills and working out the solution to such energy problems as solar power or energy-efficient improvements and make your home smarter and more sustainable.
How to Reduce Power Consumption A Smart Tips for Every Home?
It does not necessarily require complex measures to lower the electricity use in your home. With an idea of the number of watts that a house consumes and aiming at the greatest energy consumers, you can reduce costs and also decrease the carbon footprint and even prepare to use solar sources. And this is the way to make a difference.
Upgrades to Energy-Efficient Lighting
One of the least difficult spheres of improvement is lighting. Substitution of the incandescent lights with the LED lights can conserve up to 75% of the energy consumed. The LED bulbs are not only more durable but also consume less power hence they will contribute to the reduction of the average domestic power consumption.
Optimize Kitchen and Laundry Appliances
The kitchen and laundry appliances contribute some energy on a daily basis. Switch on energy saving refrigerators, microwaves and washing machines and do not use more than a few high wattage appliances simultaneously. It is possible to measure the refrigerator wattage, microwave wattage and washing machine wattage to calculate the points at which the savings can be achieved. U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA)
Manage Heating and Cooling Wisely
HVAC systems and space heaters are the most energy-consuming items. The daily energy consumption can be lowered greatly by installing smart thermostats that rely on programmable schedules and proper installation. The trick of reducing the power requirement of your home is to limit the amount of time your heater/air conditioner runs and still stay comfortable.
Reduce Standby Power from Electronics
Even unutilized electronics consume energy. Disconnection of various electronic appliances such as the TV, computer and gaming devices when they are not in use will reduce unnecessary power consumption. The awareness of the amount of electricity consumed by a TV or the amount of other electronics can help homeowners make more intelligent usage decisions.
Consider Solar Energy for Long Term Savings
In the case of bigger houses or those who use a lot of energy, solar energy is able to subsidize huge electricity bills. Nedes offers you the opportunity to save money by installating solar energy systems to use renewable energy, minimize grid dependency and save in the long-term on energy conservation.
Pro Tip
Simple daily routines, energy-saving upgrades and solar systems have the potential to significantly reduce your average home power usage significantly reduce, minimize your bills and enhance sustainability.
Conclusion
Take Control of Your Home Energy Use
The most intelligent energy planning begins with the figure of the amount of watts that a house uses. It is either a small or a big house with knowing the average power used in the house, knowing the high energy consumption appliances you can reduce the electric bills and make balanced choices on upgrades or energy saving strategies.
Paying attention to the energy consumption in your house using LED lights, appliances with the Energy Star label, smart thermostats and locating a solution to solar energy you will be able to control the energy consumption in your house and at the same time and live a more sustainable life.
Willing to switch to clean and economical energy? Get custom-made solar power systems sold by Nedes.us and start maximizing power use in your house.
FAQs
How many watts per day does a house consume?
+
In the US, the average residence has 28-33 kWh per day of electricity usage which is equivalent to about 1.2 kW of constant power usage. The daily consumption is dependent on the size of the house, the number of appliances and the frequency of use of electronics and HVAC systems.
How many kilowatts does a house use per month?
+
The average household uses 900-1000 kWh per month. The use of energy is determined by such factors as climate, population and the nature of appliances. Monthly electricity can be increased in large homes or in those that consume a lot of heavy appliances.
Which appliances in a home consume the largest amount of watts?
+
Most households use systems to heat and cool their homes which consume almost half of all the electricity. The rest of the usage consists of water heating, appliances, lighting and electronics, although HVAC often controls the daily load of energy.
How many watts does a refrigerator use?
+
Fridges usually use 150 to 400 watts based on size, model and age. The newer models which are energy saving consume less electricity and the old models or bigger fridges may end up consuming more electricity per day and this will depend on the usage of the door.
How can I lower my home’s watt usage?
+
Saving energy by turning to LED lighting disabling devices when not needed, setting the timetable of appliances, installing intelligent thermostats and thinking about using solar energy. By integrating these measures, it is possible to reduce electricity costs by a considerable margin and decrease domestic energy use.